Agile Or Traditional Project Management? Differences, Advantages and Disadvantages
| Translated by Julian Hammer
Agile project management is a flexible project management method in which projects are realized in short, iterative cycles. This allows adjustments to be made at any time and promotes the continuous improvement of product quality, teamwork and work processes.
Traditional project management follows a linear approach with clear and pre-defined phases such as planning, execution and conclusion. It focuses on predictability and fixed structures.
What is the difference between traditional and agile project management? The difference between the two methods lies in their approach to the planning and implementation of projects. While agile project management focuses on adaptability, the traditional model prioritizes stability and planning reliability.
The biggest advantage of agile project management is that it allows you to react quickly to changes like new customer requirements or changing market requirements. The disadvantage is that the course of the project can change at any time and the objectives have to be reassessed.
Traditional project management offers clear specifications and control by providing fixed milestones, detailed schedules and predefined roles and responsibilities. However, it can turn out to be inflexible if the framework conditions change.
The choice between traditional and agile project management depends on factors such as project complexity, team structure, customer requirements and the readiness for change. Projects with clearly defined goals often benefit from the traditional approach, while agile methods are a good choice for dynamic and innovative projects.
Our article offers you detailed insights into the differences, advantages and disadvantages of agile vs. traditional project management as well as into the underlying methods and principles. We also show you how the right software can support your project management.
Table of Contents
- What is agile project management?
- What is traditional project management?
- What is the difference between agile and traditional project management?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of agile and traditional project management?
- When should you use agile project management and when should you use traditional project management?
- Which is better: agile or traditional project management?
- FAQs
What is agile project management?
Agile project management is a flexible, iterative approach which is based on continuous adjustment and collaboration. The aim is to react quickly to changes and drive projects forward efficiently in order to meet the customer’s requirements as quickly and flexibly as possible. This is achieved by dividing project tasks into small task packages and gradually implementing them.
The focus is on flexibility, customer orientation, collaboration and the ability to provide functioning partial results in short cycles. These partial results promote early feedback and allows for quick adjustments to new requirements. In addition, risks can be minimized during project implementation because it is possible to identify and rectify problems at an early stage.
The core aspects of agile project management include short iterations or sprints, regular feedback, self-organized teams and close collaboration between all those involved.
The most popular agile project management methods include Scrum, Kanban, Extreme Programming (XP) and Lean. These methods have different focuses, but are all based on the principles of agility.
The Agile Manifesto from 2001 forms the basis of agile project management. It was originally conceived as a response to the rigid methods of traditional project management and defines the values and principles behind the agile working method. The Agile Manifesto focuses on flexibility, customer orientation and collaboration.
What are the core values and principles of agile project management?
The values of the Agile Manifesto form the basic orientation of agile project management, while the principles substantiate how these values can be implemented in practice. They serve as guidelines for an agile way of working by clearly defining both the attitude and the implementation steps.
The core values of agile project management can be described as follows:
- Individuals and interactions via processes and tools: The focus is on effective cooperation between team members, as this has a significant influence on the success of the project.
- Functioning software and project results via comprehensive documentation: The delivery of a functioning product has top priority. Documentation remains important, but should not hinder the progress of development.
- Cooperation with the customer on contract negotiations: Close and continuous cooperation with the customer ensures that their needs are met and that the end product meets their expectations.
- Responding to change by following a plan: Flexibility and the ability to react to change are crucial to being successful in a dynamic environment.
Based on these values, frameworks such as Scrum and Kanban were developed to put agile principles into practice.
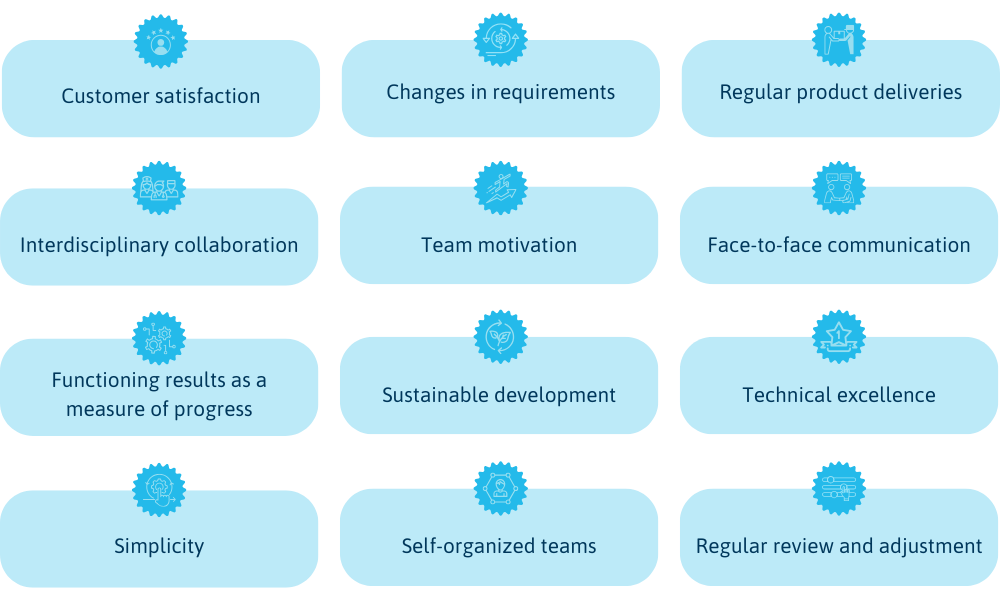
The 12 principles of the Agile Manifesto are:
- Customer satisfaction through early and continuous delivery: Customer satisfaction is paramount. Partial results are therefore provided on a regular basis.
- Positive reception of changes in requirements: Even late changes to requirements are welcomed in order to give the customer a competitive advantage.
- Delivery of functioning results in short periods of time: Functioning project results are delivered regularly at short intervals, with shorter periods of time being preferred.
- Daily collaboration between technical experts and developers: Businessmen and developers work together on a daily basis during the project to achieve optimal results.
- Deploy motivated individuals in projects: Projects are staffed with motivated people who receive the necessary support and trust to fulfill their tasks.
- Efficient face-to-face communication: The most effective method of conveying information is face-to-face conversation.
- Functioning results as a measure of progress: The primary progress indicator is the delivery of the partial results achieved.
- Promote sustainable development: Agile processes promote sustainable development in which clients, developers and users can maintain a steady pace indefinitely.
- Striving for technical excellence: The compliance with high technical standards and a well thought-out design facilitate flexible working.
- Simplicity is decisive: The focus is on concentrating on what is necessary and reducing the workload.
- Self-organized teams: The best architectures, requirements and designs are created in self-organized teams. They can work independently, react flexibly to changes and make optimum use of the expertise of all team members.
- Regular reflection and adjustments: The team reflects at regular intervals on how it can become more effective and adapts its behavior accordingly.
What agile methods and frameworks are there?
Agile methods offer flexible approaches for project management and product development. These methods include:
- Scrum
- Kanban
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Lean
- Scrumban
- Objectives and Key Results (OKRs)
- Design Thinking
- Feature-Driven Development (FDD)
- Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
- Spotify Model
Below we present to you the three most important agile methods:
- Scrum is a framework that is designed to divide complex projects into iterative work steps. The work is carried out in so-called sprints, which generally have a duration of two to four weeks. The central roles include the product owner who prioritizes the requirements, the Scrum master who supports the team and removes obstacles, as well as the development team that realizes the work. Typical components of Scrum are daily stand-up meetings, sprint planning, reviews and retrospectives.
- Kanban is a method for the visualization and controlling of work processes. The workflow is optimized in order to identify bottlenecks at an early stage. Work stages are displayed on a Kanban board, showing different phases such as “To do”, “In progress” and “Done”. There are no fixed roles and the focus is on flexibility and the continuous improvement of the project schedule. A central component is the limitation of simultaneously running tasks (Limit Work in Progress) in order to increase efficiency.
- Extreme Programming is a method that aims at achieving high-quality results through short development cycles and continuous customer feedback. Techniques such as pair programming, test-driven development and frequent releases are typical features. The aim is to adapt quickly to new requirements while ensuring high quality at the same time.

In addition to these methods, there are many other approaches and project management strategies that are tailored to meet individual requirements. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages and is suitable for different scenarios. The choice of the right method should always be based on the objectives and needs of the project to ensure a maximum of efficiency and success.
What is traditional project management?
Traditional project management is a linear approach in which projects run in clearly defined phases that build on one another.. These phases typically include the initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and conclusion of a project.
The aim of traditional project management is to complete projects efficiently and with minimal risk through detailed planning and control.
The focus areas of traditional project management are comprehensive planning, clear specifications and adherence to time, cost and quality targets. Core aspects are fixed structures, a clear project plan, defined responsibilities and a controlled process.
The most important principles of traditional project management are:
- Clear target definition: project objectives are clearly defined at the beginning.
- In-depth planning: each project step is thought through and planned in advance.
- Fixed milestones: progress is reviewed at defined points.
- Risk management: risks are identified and managed.
- Strict control: monitoring time, budget and quality throughout the project.
- Documented conclusion: the project ends with a complete handover and documentation.
Popular methods that originate from traditional project management include the waterfall model, milestone planning, the Critical Path Method (CPM), Gantt charts and PRINCE2.
Traditional project management offers a fixed structure and is particularly effective for projects with clear requirements and little need for change. Traditional project management has proven itself above all in projects with a physical project objective such as the creation of a product. Traditional project management is used when it comes to complying with the legal requirements and regulations. If several projects are realized simultaneously, we speak of multi-project management.
What Are the Core Values and Principles of Traditional Project Management?
Traditional Project Management is Based on the Following Values:
- Plannability: Projects are structured by in-depth planning and the defintion of clear objectives. This ensures a high degree of predictability in the course of the project and minimizes risks.
- Stability: fixed requirements, processes and schedules provide security and structure. Changes during the project are avoided as far as possible so as not to disrupt the course of the project
- Control: progress is continuously monitored to identify deviations at an early stage and take targeted countermeasures.
- Efficiency: resource management is optimized through clear guidelines and defined responsibilities in order to meet time and budget targets.
Specific requirements have a decisive impact on the course of the project. They allow for precise planning and prevent unnecessary adjustments which can increase time and costs. At the same time, they require possible risks and changes to be taken into account as early as the planning phase, as subsequent adjustments can be costly.
In traditional project management, the project manager plays a central role in controlling and monitoring. The project manager ensures that all project participants meet the specified targets and that schedules and budgets are adhered to. Modern tools support project management with automatic reports and clearly organized status reports that provide insight into project progress at the click of a button. This allows deviations to be identified and corrected at an early stage.
Hierarchies and clear responsibilities are particularly important in traditional project management, as they ensure that everyone involved knows what tasks they have to perform and who makes decisions. This increases efficiency and minimizes misunderstandings, particularly in large-scale, complex projects.
What Traditional PM Methods and Frameworks Are There?
Traditional project management encompasses a variety of methods that aim to control projects by using clear structures, detailed planning and strict control.
Traditional project management methods include:
- Waterfall model
- PRINCE2
- PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge)
- Milestone planning
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Gantt charts
- PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique)
- Earned Value Management (EVM)
- Six Sigma (DMAIC)
- Event Chain Methodology (ECM)
- Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)
- International standard ISO 21500
- V‑Model
- Top-down and bottom-up planning
These methods offer different approaches to systematically manage and control projects.
The three most important traditional approaches — the waterfall model, PRINCE2 and PMBOK — are explained in more detail below.
- The waterfall model is a linear method in which each project phase is entirely completed before the next phase starts. The phases typically comprise requirements analysis, planning, design, implementation, test and maintenance. It is characterized by a clear sequence and fixed milestones. The aim is to complete projects in a stable manner and on schedule by defining all requirements at an early stage. Since changes are hard to implement during the course of the project, the waterfall model is particularly suitable for projects with known requirements that are not subject to changes.
- PRINCE2 (Projects in Controlled Environments) is a process oriented framework in which projects are managed with the help of defined roles, clear phases and a structured procedure. It attaches great importance to the management of resources and the monitoring of progress through regular reports. The central roles include the project manager, the project steering commitee and the project team. The method divides projects into controllable sections and emphasizes responsibility at all levels. PRINCE2 is suitable for a variety of project types and is often used in strongly regulated sectors.
The PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) framework is a comprehensive guideline that defines proven practices and standards for project management. It describes five process groups: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and management as well as the conclusion of the project. Furthermore the PMBOK defines ten areas of knowledge, including time management, cost management and quality management. PMBOK is not a rigid method but a flexible framework that can be adapted to the requirements of specific projects. The goal is to implement projects in an efficient and standardized manner.
What is the difference between agile and traditional project management?
Agile and traditional project management follow different approaches, especially with regard to project planning, organization and dealing with changes. In the agile approach, planning is done step by step. This results in a flexible project that runs in short cycles, known as sprints. In contrast, traditional project management is based on fixed, detailed planning with a clearly defined time frame that is specified from start to finish.
Due to their step-by-step approach, agile projects are designed to continuously adapt to new requirements. Changes can be integrated at any time in order to react flexibly to external factors such as market changes or new customer requirements and to ensure customer benefits.
In traditional project management, on the other hand, changes are often expensive and time-consuming. The planning and structure of the projects are not designed for flexible adjustments. Resources and deadlines must first be rescheduled in the linear process, which can delay the entire course of the project and cause additional costs. This makes it difficult to react quickly to new requirements or changes in the market.
Another difference lies in the organization of the teams. Agile teams are self-organized and make decisions collectively, which makes collaboration more dynamic and flexible. Traditional teams, on the other hand, work hierarchically with clearly defined roles and responsibilities, whereas decisions are usually made by the project management.
Agile teams hold regular meetings such as daily stand-ups to discuss the progress and get quick feedback. In traditional project management, on the other hand, feedback is often only provided in certain phases, such as after milestones or at the end of the project, limiting the possibility for short-term adjustments.
In the table below, we summarize the differences between agile and traditional project management.
| Criterion | Agile project management | Traditional project management |
|---|---|---|
| Project structure and planning |
|
|
| Flexibility and changes |
|
|
| Roles and responsibilities |
|
|
| Communication and feedback |
|
|
| Customer involvement |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of agile and traditional project management?
Agile project management offers numerous advantages. A key advantage is the flexibility and adaptability to changing requirements. This enables projects to respond to new market conditions and customer requirements. Short development cycles and regular meetings also allow for rapid feedback. This uncovers errors at an early stage and facilitates optimization to achieve high-quality results. Another advantage is the continuous involvement of the customer. This ensures close cooperation and increases customer satisfaction because the result is better tailored to the customer’s needs.
However, there are also disadvantages. In the agile approach, the time and budget planning is more demanding since project requirements can change. This makes the effort difficult to calculate. Agility also requires a high degree of discipline and self-organization in the team. This can be a challenge, especially for inexperienced or heterogeneous teams. Since clear structures and fixed responsibilities are often lacking, agile projects can become confusing.
Traditional project management also offers numerous advantages. A significant advantage is the clear structure and plannability. This is particularly advantageous for large projects, as each phase is precisely defined and coordinated. The traditional model is also suitable for projects with stable requirements in the course of which no substantial changes are expected to take place. Another advantage is the simple control over time and costs. Thanks to detailed planning and monitoring, deviations are recognized and controlled at an early stage.
Despite these advantages, traditional project management also comes with some disadvantages. One disadvantage is the lack of flexibility due to difficulties in the implementation of changes which often cause additional costs and delays. This makes the traditional model less suitable for dynamic projects that require adjustments. Furthermore there is the risk of changing requirements which result in the project no longer meeting current needs. It is conceptualized for a fixed plan that is difficult to adapt during implementation.
In the following table you can see the advantages and disadvantages of agile and traditional project management at one glance:
| Category | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Agile project management |
|
|
| Traditional project management |
|
|
When to use agile project management and when to use traditional project management?
Traditional project management is particularly suitable for projects with stable requirements and clearly defined goals. It is often used in highly regulated industries such as construction, aviation or the manufacturing industry; in other words, wherever a high degree of planning capability and precision is required. Projects in which fixed time and budget frames are crucial, such as the construction of a building or the development of a technical product, also benefit from the linear structure of the traditional approach. The focus here is on clear specifications, detailed planning and strict control.
Agile project management, on the other hand, is particularly suitable for dynamic projects in which requirements can vary during implementation. It is often used in innovative and fast-moving industries such as software development, marketing or product development. Companies that place a high value on flexibility and the ability to adapt quickly to market changes benefit from the iterative working method. Examples include the development of new apps, the introduction of creative marketing campaigns or the continuous improvement of services. Agile approaches are ideal when customer requirements must be adjusted in the course of the project and fast results are needed.
Besides traditional and agile approaches, there are also hybrid models which combine elements of both methods. These are suitable for projects that require both a fixed structure and flexibility.
What is hybrid project management and how does it combine both approaches?
Hybrid project management is an approach that combines agile and traditional methods. It combines the linear and structured planning of traditional project management with the flexibility and adaptability of the agile approach. This allows teams to efficiently plan projects with stable framework conditions, while at the same time integrating dynamic elements to react flexibly to changes or new requirements.
Hybrid approaches are often used to exploit the advantages of both methods. The clear structure and predictability of the traditional approach offers security and a reliable basis. Agile elements such as iterative processes and rapid feedback make it possible to make adjustments and increase customer satisfaction. This combination is particularly suitable for projects that require both fixed specifications and flexibility, e.g. in product development or in large-scale IT projects.
Which is better: agile or traditional project management?
Agile and traditional project management differ mainly in their approach to planning, structure and adaptability. While agile project management is flexible and iterative and generally well suitable for dynamic projects, the traditional model relies on a clear, linear structure, making it ideal for projects with stable requirements.
The choice of the method depends on the project specifications. Agile project management is suitable when flexibility is required and the criteria can change during the project. Traditional project management is useful when fixed schedules and strict control are required. However, there is no “one-size-fits-all” model. Hybrid project management combines the advantages of both approaches and is therefore usually best suited to cover the various objectives.
The ability to adapt to changing requirements while maintaining stability in planning is crucial to the success of the project. The best method is therefore often a combination of agile and traditional approaches that are tailored to the specific needs of the project.
There are particular software solutions such as PLANTA Project as a Hybrid System. This tool optimally supports both traditional and agile project management as well as hybrid approaches. It offers functions such as waterfall schedules, Scrum boards and Kanban visualizations. Furthermore it allows for the integration of both approaches in one project and offers flexible reports to map the progress in a transparent way.
FAQ
Is it possible to combine agile and traditional project management?
Agile project management is based on the values and principles of the Agile Manifesto and can be combined with traditional project management to benefit from the advantages of both approaches. Clear structures and predictability meet flexibility and iterative working methods, which enables efficient adaptation to different project requirements.
For what type of projects is agile project management unsuitable?
Agile project management is unsuitable for projects with fixed requirements, strict schedules or highly regulated framework conditions such as the construction industry or aviation. Important metrics for measuring success are customer satisfaction, speed of completion (lead time) and adherence to budget and quality.
What industries use traditional project management the most?
Traditional project management is often used in aviation, in construction and in the automotive industry, especially for projects with long development cycles and extensive waterfall plans, e.g. up to model-readiness. However, even highly regulated sectors such as the pharmaceutical industry are increasingly relying on hybrid approaches in order to operate more flexibly.
With us, you don’t have to choose!
Whether you manage your projects in an agile or traditional way. Decide on the right method for each project — or combine the best of both in hybrid project management.
This blog post has been translated by Julian Hammer
Related Posts
RECENT POSTS
Create a Project Plan in 10 Steps — Using a Checklist
Jochen Geißer2025–07-03T07:46:33+00:0017. June 2025|
Phases of Project Management: the 5 Project Phases in Detail
Larissa Plank2025–06-16T09:14:02+00:005. June 2025|
Resource Planning in Multi-Project Management: a Guideline
Beate Schulte2025–05-22T08:18:10+00:0022. May 2025|














